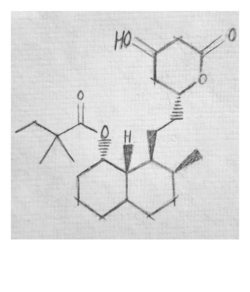
Simvastatin
Simvastatin is the second-most widely used cholesterol drug. Over 48 million prescriptions are filled every year in the US alone.
Simvastatin is available in 5, 10, 20, 40, and 80 mg tablets. The daily dosing range is 5-80 mg with a recommended starting dose of 20 to 40 mgs daily, taken with meals.
In 2010, the Food and Drug Administration issued an advisory on the risk of side effects from the highest dosage (80 mg/day) of simvastatin. In June 2011 the agency said that dosage should not be given to new patients because of reports of myopathy.
Simvastatin in the Body
Most of the medicine is absorbed in the intestine. About 15% typically exits through the feces. Once in the bloodstream, most is metabolized. A little is removed by the kidneys. After ingestion, peak bloodstream concentration is in 80 to 160 minutes. Simvastatin has a shorter half-life in the body than atorvastatin.
 Researchers have found the drug starts to work several days after the patient starts taking it and peaks in about 2 weeks, leveling off if a constant dosaging is maintained.
Researchers have found the drug starts to work several days after the patient starts taking it and peaks in about 2 weeks, leveling off if a constant dosaging is maintained.
This drug is not approved for pregnant women, and there is some indication that cholesterol synthesis may be important in fetal development, so statin drugs should definitely not be given. If pregnancy occurs during treatment, alert your doctor, who will almost certainly discontinue simvastatin.
Patients who drink large amounts of alcohol or have a history of liver disease are sometimes not prescribed simvastatin because of concerns about the drug's effect on the liver.
Like other statins, simvastatin can be taken with meals. Generally the drug should be taken in the evening or night to increase efficacy.
Brand Names for Simvastatin
Simvastatin was developed in 1981 and patented by Merck & Co. Simvastatin was first approved for use in Sweden in 1988; it did not receive United States FDA approval until December of 1991. Merck sold it under the brand name Zocor and had exclusive rights until the patent expired in 2006. Other companies can now make simvastatiin as it has "gone generic". Only Merck can still use the name Zocor, however.
Simvastatin for Primary Prevention
One way to divide patients is between those who have had specific CVD events and those who have not. If someone has experienced a stroke or heart attack, we say the statins are given for secondary prevention. The goal is to prevent another event. People who have never had such an event can be given statins as primary prevention. Primary prevention patients are the higher-hanging fruit. There is a benefit from treating them, but it is not as great on average as the benefit from treating people who have already had heart attacks.
Facts
Formula: C25H38O5
Category: semi-synthetic, Type I
Manufacture: fermentation
Solubility: lipid
Introduction: 1992
Brands: Zocor, Zocord, Zimstat, Simvacor, Simvaxon, Lipovas, Simlup, Simvotin, Simcard, Lodales.
The presence of food in the stomach can change drug absorption and exposure. Most of the time food with a high fat content increases the drug AUC. Another metric you see in pharmacokinetics is area under the curve (AUC), which is borrowed directly from calculus. If you plot concentration of the drug in the blood over time, the area under that curve is sort-of, sometimes, and indicator of total drug exposure.
Simvastatin is also part of the combination pill Vytorin. More on that here.
Scientists in Taiwan have experimented using simvastatin as a treatment for skin cuts, to see if it would to stop staph infections. They found simvastatin kept the infection away for 8 hours and speculated it could be used as a disinfectant.
People have long known statins decrease the incidence of atrial fibrillation but nobody really knows why. Atrial fibrosis leads to atrial fibrillation so some scientists speculated simvastatin would be associated with a slowing in atrial fibrosis. In a paper published in Circulation Research researchers indicated simvastatin inhibits proliferation and activation of cardiac fibroblasts.
It has been suspected that statins make exercise more difficult, or at least less effective. A study published in the that Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that simvastatin not only limits increases in cardiovascular fitness, but also slows the increases in mitochondria in the skeletal muscles that would normally occur.
Although there had been hope that statins could be effective in treating people with COPD pLINK[ a large study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found simvastatin had little effect on moderate-to-severe COPD. The study also suggested simvastatin had little effect on lungs in general.
British scientists found simvastatin given to multiple sclerosis patients helped slow the rate of brain atrophy. Further testing is needed before this becomes a standard treatment, but given the low side effects and general safety of simvastatin, the prospects are good.
The long speculated effect of statins on the development (or lack thereof) of Alzheimers’ Disease got some support when scientists found simvastatin which are known to occur in high quantities in brains with Alzheimers.
Because statins reduce inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis, interest in their use for patients with muscular dystrophy has been raised. Recent work with simvastatin has found that drug can help these patients.
Simvastatin is not benenficial in treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Research
Simvastatin as a treatment for pulmonary hypertension trial.
Simvastatin in the treatment of asthma: lack of steroid-sparing effect.
FDA; Simvastatin Used With Amiodarone Safety