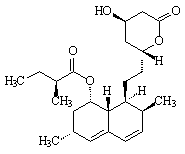
Lovastatin
Lovastatin (brand names Mevacor, Altocor, and Altoprev) was the first statin approved for human use. In 1978, lovastatin (originally called mevinolin) was isolated from the fungus Aspergillus terreus by scientists working Merck Research Laboratories. Merck subsequently developed simvastatin, which is a close chemical derivative and they promoted this drug, which had a later patent expiration date. Lovastatin is not widely used any more as it is considered less effective than second-generation statin drugs atorvastatin and simvastatin.
Lovastatin was one of the great success stories of modern pharmacology. In clinical trials in the early 1980s, treatment with lovastatin dramatically reduced patients’ LDL levels, in addition to reducing plasma triglycerides, and slightly increasing HDL “good cholesterol” levels. Safety and tolerability were excellent. Spurred by these results, Merck applied for regulatory approval for lovastatin in 1986. The FDA approved lovastatin in July 1987. Merck’s patent expired in 2001; generics are now currently available. In 2002 an extended release formulation was approved by the FDA; originally marketed as Altocor, the name was changed to Altoprev in 2004.
Lovastatin is available in 10, 20 and 40 mg tablets. The typical starting dose is 20 mg, given in the evening with food. The maximum recommended dose is 80 mg/day.
Although not used widely for cholesterol or cardiovascular issues anymore, lovastatin continues to attract interest of researchers for possible use in treatment of cancer and bone diseases. Red yeast rice contains an estimated 2.4 mg lovastatin per 600 mg rice.
Facts
Formula: C24H36O5
Category: synthetic, Type I
Manufacture: chemical synthesis
Solubility: lipid
Introduction: 1987
Brands: Mevacor, Advicor, Altoprev
Lovstatin may find its way into bone medicine, too. Scientists have injected it into a polyurethane scaffolding to stimulate repair of bone fractures in animals.
Lovastatin can induce cell death in cancer tumors but it is not used in cancer therapy. A trial to see if lovastatin affected biomarkers for breast cancer found no effect.
People are even trying to use lovastatin for depression treatment although it has not found its ways into practice. And for attention disorders.