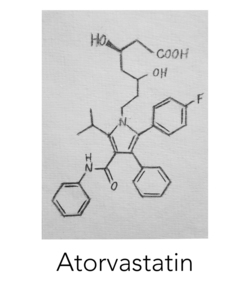
Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
Atorvastatin is the most widely used statin drug. Sold under the brand name Lipitor it was the biggest of the blockbuster drugs of the 21st Century and the single biggest selling pharmacentical (in terms of retail sales) ever. The patent has expired and the pharmaceutical industry has made this drug avaolable in a generic form. The number of prescriptions in the US every year is over 112 million. making it the most prescribed drug.
The long-term benefits of atorvastatin have been demonstrated in scientific study after study. In one European study, patients who had been given low (10 mg/day) doses of atoravastain were revisited by researchers long after the study was finished. Compared to untreated patients, the statin patients had lower death rates from even non-cardiovascular causes. These include respiratory problems and other common causes of death which the antiinflammatory effects of atorvastatin may help.
 Many studies have established the effectiveness and safety of atorvastatin. Scientists have followed the health of tens of thousands of people on this medicine, in different countries. It lowers the mortality and risk of heart disease in patients with a history of cardiovascular problems. Whether it should be prescribed for patients with no history of problems or certain risk factors is a matter of debate within the medical community.
Many studies have established the effectiveness and safety of atorvastatin. Scientists have followed the health of tens of thousands of people on this medicine, in different countries. It lowers the mortality and risk of heart disease in patients with a history of cardiovascular problems. Whether it should be prescribed for patients with no history of problems or certain risk factors is a matter of debate within the medical community.
Atorvastatin interacts with many other drugs. Be sure to tell your doctor about ALL prescription drugs and over-the-counter drugs that you take. Patients with a history of hemorrhagic stroke may be at increased risk for another stroke.
Like all statins, atorvastatin works in the liver, by inhibiting enzymes that make cholesterol. It also have anti-inflammatory effects. It is taken as a pill, and the concentration of the drug in the bloodstream peaks an hour or two after the pill is ingested. Guidelines suggest you eat a little food with the pill as this tends to slow the absorption from the digestive system. Almost all the atorvastatin in the blood becomes bound to plasma proteins. In this way, the medicine and cholesterol are similar in the way they travel in the bloodstream.
Some scientists have raised concerns about the long term risks of atorvastatin usage. Controlled trials run to support regulatory approval do not ordinarily extend to studying long-term use. Polypharmacy - the patient use of multiple medications - is more prevalent in older persons, and this is of some concern.
Atorvastatin Regimen
The commercial preparation is atorvastatin calcium. (The calcium is the anion part of the salt. Prescription drugs are frequently sold as salts. This drug is not a major source of dietary calcium.)
Atorvastatin is available in 10, 20, 40, and 80 mg tablets. Most patients take 10 or 20 mg per day. Your doctor will prescribe a dosage based on many factors. Some patients need 40 mg/day and 80 mg daily is given to patients with acute coronary syndrome.
Atorvastatin in the Body
The medicine is absorbed in the intestine and once in the bloodstream, most is metabolized. Less than 2% is removed by the kidneys. After ingestion, peak bloodstream concentration is in 60 to 120 minutes. The half-life is 14 hours for atorvastatin. The half-life is longer than the half-life of simvastatin. Unlike that drug, atorvastatin can be taken in the morning because of its long half-life, but most doctors recommend it be swallowed in the evening.
The presence of food in the stomach can change drug absorption and exposure. Most of the time food with a high fat content increases the drug AUC. AUC is area under the curve, which is borrowed directly from calculus. If you plot concentration of the drug in the blood over time, the area under that curve is sort-of, sometimes, and indicator of total drug exposure.
The drug starts to work several days after the patient starts taking it and achieves peak blood concentrations in about 2 weeks, leveling off if a constant dose is maintained,
Atorvastatin is not approved for pregnant women, and is not considered safe for fetuses.
Like other statins, atorvastatin can be taken with meals.
Patients who drink large amounts of alcohol or have a history of liver disease are sometimes not prescribed atorvastatin because of concerns about the drug's effect on the liver.
Side effects
Like other statins, the side effects that are of most concern involve the liver (requiring periodic check of transaminase levels in the blood) and muscle damage. FDA analysis has concluded liver injury is rare. Other common atorvastatin side effects are diarrhea, joint pain, and inflammation and pain in the pharynx and larynx.Atorvastatin for Stroke Prevention
Statin medications reduce the risk of stroke in people with vascular disease. Incidences of ischaemic stroke decline, but probably not those of hemorrhagic stroke. Further, even after people have had a stroke or transitory ischemic attack, using statins reduces the risk of a second stroke.Note that epidemiological studies have not shown a definitive association between cholesterol levels and stroke. It is possible that however statins stop strokes is through a different mechanism than how they reduce heart disease risk.
Patent expiration
The pharmaceutical company Pfizer held the US patent on atorvastatin for years and sold the medicine under the brand name Lipitor. They sold billions of dollars of Lipitor. It was Pfizer's biggest selling product and indeed the single biggest selling drug (in terms of revenues) during the 2000s. Pfizer reportedly sold $10.7 billion worth of Lipitor in 2010. $7 billion was from the U.S. alone, where 3.5 million people took the drug.
In November 2011 the patent expired and the drug companies Watson and Ranbaxy now sell atorvastatin in the US. Ranbaxy now sells more atorvastatin pills than Pfizer does.
Other sellers must still meet government standards for safety and efficacy. The price of the generic atorvastatin is substantially lower than the price of branded Lipitor. If you still take branded Lipitor, ask your doctor or insurance company about switching to the generic version. Also be sure to check different retail pharmacies in your area because the price of even the generic form can vary considerably.
Facts
Formula: C33H35FN2O5
Category: synthetic, Type I
Manufacture: chemical synthesis
Solubility: water
Introduction: 1996
Brands: Lipitor, Atovarol, Tahor, and Sortis
A combination of atorvastatin and the calcium channel blocker high blood pressure drug amlodipine is sold under the name Caduet.
Research
Structure-activity relationship of atorvastatin derivatives for metabolic activation by hydrolases.